Company ethics examples, often referred to as business ethics, encompass the moral principles and standards that guide behavior within the business world. These principles help companies determine what is right and wrong, guiding their decisions and actions. Ethical practices in a company cover a wide range of areas, including but not limited to, honesty, integrity, fairness, respect, transparency, and responsibility. The significance of company ethics lies in establishing a framework for ethical decision-making, which is vital in navigating the complex and often challenging world of business.
Relevance:
The relevance of ethics in companies cannot be overstated. Ethically sound companies are more likely to earn and maintain the trust of their customers, employees, and the public. This trust translates into various tangible benefits, such as customer loyalty, enhanced brand reputation, and an overall positive corporate image. Furthermore, ethical practices ensure legal compliance, helping companies avoid legal repercussions that might arise from unethical behavior. Adhering to ethical standards also fosters a positive workplace environment, which can lead to increased employee morale, higher productivity, and reduced turnover rates. In an increasingly socially conscious world, a company’s commitment to ethics can be a defining factor in its long-term success and sustainability.
Table of Contents
Key Principles of Company Ethics
Integrity:
Integrity is a cornerstone of ethical business practice. It involves upholding honesty and strong moral principles. In business operations, integrity means conducting affairs in a truthful and straightforward manner. This includes honoring commitments, avoiding deceptive practices, and maintaining consistency between words and actions. The importance of integrity lies in its ability to build trust with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and business partners. A company known for its integrity is more likely to attract and retain loyal customers and employees, as it fosters a reputation of reliability and ethical soundness.
Transparency:
Transparency in business is about being open, clear, and communicative about various aspects of operations, decisions, and business practices. This principle emphasizes the importance of sharing relevant information with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors, in a straightforward and accessible manner. Transparency builds trust, as it allows stakeholders to understand the motives, values, and practices of the company. This openness helps in creating an environment of mutual respect and trust, and can also contribute to preventing misunderstandings and managing potential conflicts more effectively.
Fairness:
Fairness in company ethics pertains to equitable treatment of all parties involved with the company. This includes employees, customers, suppliers, and competitors. Fairness involves making decisions that are just, impartial, and not self-serving. Companies that practice fairness in their dealings are seen as trustworthy and responsible. It is crucial in creating a level playing field in the market, ensuring equal opportunities, and fostering a healthy competitive environment. Fairness also relates to internal practices, such as offering equal opportunities for employee advancement and maintaining a non-discriminatory work environment.
Accountability:
Accountability in company ethics refers to the obligation of companies to be answerable for their actions. This principle demands that companies accept responsibility for the consequences of their decisions and actions, both positive and negative. It involves transparently reporting company performance and admitting mistakes when they occur. The concept of accountability extends to adhering to legal and regulatory standards, ethical codes, and societal expectations. A culture of accountability within a company promotes responsible behavior, enhances credibility, and can lead to improved decision-making processes. It also reassures stakeholders that the company is committed to ethical practices and continuous improvement.
Examples of Company ethics examples
Patagonia:
Patagonia stands out as a leader in environmental sustainability and ethical labor practices. The company’s commitment to the environment is evident in its use of sustainable materials and processes, as well as its efforts to minimize its ecological footprint. Patagonia is known for its transparency in supply chain management, ensuring that its products are produced under fair labor conditions. Moreover, it actively engages in environmental activism, supporting various environmental causes and encouraging customers to buy only what they need, an unusual stance for a retail company. Patagonia’s dedication to these principles has made it a model for sustainable and ethical business practices.
Ben & Jerry’s:
Ben & Jerry’s is renowned for its commitment to social justice and environmental sustainability. The company has been involved in numerous social justice campaigns, advocating for issues like climate change, racial equality, and refugee rights. In terms of sustainability, Ben & Jerry’s sources its ingredients responsibly, prioritizing suppliers that meet high environmental and social standards. The company has also made significant efforts to reduce its carbon footprint, including using eco-friendly packaging and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. This blend of activism and ethical business practices has positioned Ben & Jerry’s as a leader in corporate social responsibility.
LEGO:
LEGO’s approach to ethical business practices is centered around product safety and ethical supply chain management. The company places a high priority on ensuring that its products are safe for children, adhering to stringent safety standards. LEGO has also shown a strong commitment to ethical supply chain practices. This includes ensuring fair labor practices and working conditions in its factories and being transparent about its sourcing policies. In addition, LEGO has made strides in sustainability, such as committing to using sustainable materials in its products and reducing its overall environmental impact. LEGO’s commitment to these ethical principles has not only enhanced its brand reputation but also set a standard in the toy industry for responsible business practices.
Case Studies of Company ethics examples
Employee Welfare Programs:
Many companies have distinguished themselves through exceptional employee welfare programs, recognizing that the well-being of their employees is central to their success. For example, Salesforce has been lauded for its holistic approach to employee welfare, offering substantial benefits like comprehensive health plans, generous parental leave, and mental health days. Google is another prime example, known for its innovative and employee-friendly work environment, which includes on-site wellness and healthcare services, flexible work hours, and an emphasis on work-life balance. These companies demonstrate that investing in employee welfare not only enhances productivity and job satisfaction but also attracts and retains top talent, creating a strong and motivated workforce.
Community Engagement:
Corporate engagement in community development and charitable initiatives is another key aspect of ethical practices. Microsoft, through its philanthropic arm, Microsoft Philanthropies, actively contributes to global community development, focusing on education, poverty alleviation, and disaster response. Similarly, Starbucks’ community service efforts include supporting local initiatives, promoting volunteerism among employees, and contributing to disaster relief efforts. These activities not only benefit the communities but also strengthen the companies’ reputations as socially responsible entities.
Environmental Initiatives:
Regarding environmental responsibility, IKEA has made significant strides in reducing its carbon footprint and investing in renewable energy. The company aims to become climate positive by 2030, focusing on sustainable product design and renewable energy initiatives. Another example is Tesla, which is at the forefront of reducing carbon emissions through its electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions. These companies have integrated environmental sustainability into their core business strategies, setting an example for others in their industries and beyond. Their initiatives demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices that extend beyond profit, addressing broader environmental challenges.
The Impact of Unethical Practices
Unethical behavior in business can have severe and long-lasting consequences. The cases of Enron and Volkswagen serve as stark examples. Enron’s scandal, marked by accounting fraud and corruption, led to the company’s collapse, eroding investor confidence and leading to significant legal repercussions. The scandal not only resulted in substantial financial loss but also tarnished the reputation of those involved, highlighting the devastating impact of unethical corporate behavior.
Volkswagen’s emission scandal is another instance where unethical practices had dire consequences. The company’s decision to manipulate emission tests for their diesel vehicles not only resulted in hefty fines and legal actions but also severely damaged its reputation. The long-term impacts of such unethical behavior include loss of customer trust, diminished brand value, and ongoing financial struggles. These examples underscore the importance of ethical conduct in maintaining a company’s reputation and financial stability.
Strategies for Maintaining Company Ethics
Ethics Training:
Regular ethics training for employees is crucial in maintaining an ethical corporate culture. Such training helps employees understand the company’s ethical standards and how to apply them in their daily work. It also provides guidance on handling ethical dilemmas and reinforces the importance of ethical behavior in the workplace. Consistent ethics training ensures that all employees are aligned with the company’s ethical values and principles, reducing the risk of unethical behavior.
Ethical Leadership:
Leadership plays a pivotal role in setting and upholding ethical standards within a company. Leaders who demonstrate ethical behavior set a positive example and create an environment where ethical practices are valued and encouraged. Ethical leadership involves not only adhering to high moral standards but also being transparent, accountable, and fair in decision-making processes. Leaders who prioritize ethics inspire their teams to follow suit, fostering a culture of integrity and trust.
Regular Auditing:
Implementing regular audits is an effective way to maintain ethical practices. Audits help in identifying any areas of ethical concern, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory standards, and assessing the effectiveness of existing ethics policies. Through these audits, companies can proactively address potential ethical issues, implement corrective measures, and continuously improve their ethical standards. Regular auditing also demonstrates to stakeholders that the company is committed to ethical conduct and transparency.
An Info graph for Company ethics examples
Here is the infographic illustrating company ethics examples. It includes key principles such as integrity, transparency, fairness, and accountability, alongside examples of ethical companies like Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, and LEGO. The infographic also covers the impact of unethical practices with cases like Enron and Volkswagen, and strategies for maintaining ethics in companies.
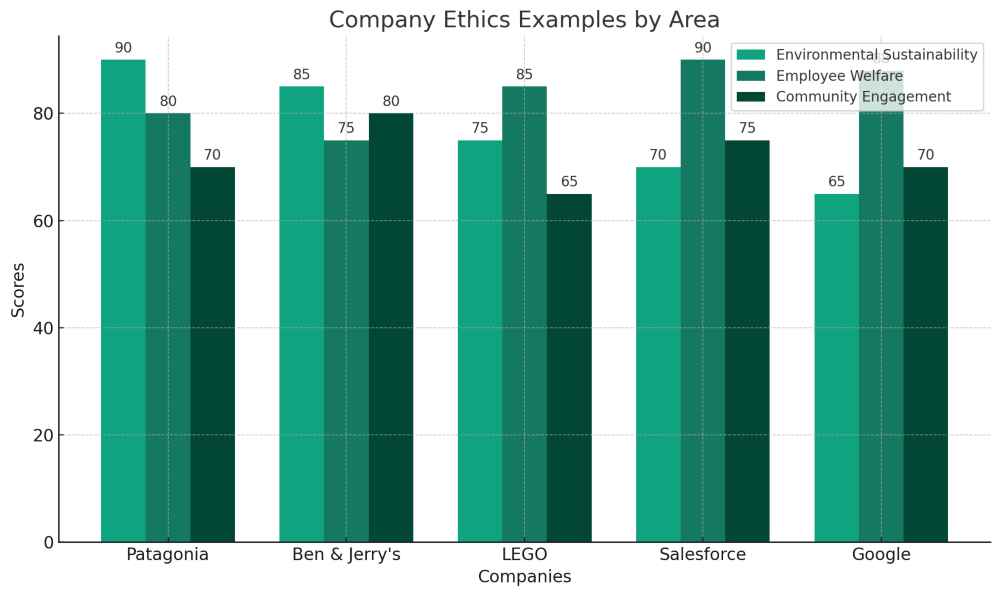
A graph for Company ethics examples
Here is a bar graph representing company ethics examples in different areas. The graph compares five companies – Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, LEGO, Salesforce, and Google – across three ethical areas: Environmental Sustainability, Employee Welfare, and Community Engagement. Each company’s score in these areas is represented, providing a visual comparison of their performance in terms of ethical practices.
A Chart table for Company ethics examples
To create a chart table for company ethics examples, I’ll use a table format that outlines various ethical aspects and the corresponding performance or initiatives of different companies. The table will include columns for the company name and various ethical categories like environmental sustainability, employee welfare, and community engagement. Here’s how the data might be structured:
| Company | Environmental Sustainability | Employee Welfare | Community Engagement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patagonia | High Commitment | Strong Programs | Active Participation |
| Ben & Jerry’s | Sustainable Sourcing | Good Benefits | Social Advocacy |
| LEGO | Eco-Friendly Materials | Excellent Safety | Community Projects |
| Salesforce | Carbon Neutral Goals | Comprehensive Benefits | Philanthropy |
| Renewable Energy Use | Work-Life Balance | Global Initiatives |
This table will provide a snapshot of how each company performs or contributes in these key areas of ethics. Let’s create a visual representation of this table.
Here is the chart table that outlines the company ethics examples for Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, LEGO, Salesforce, and Google. The table includes their performance or initiatives in key ethical areas: Environmental Sustainability, Employee Welfare, and Community Engagement. This format provides an overview of each company’s contributions and practices in these important ethical dimensions.
Summary:
This article explored the critical importance and various dimensions of company ethics. We began by defining company ethics and its significance in the corporate world, emphasizing how ethical practices foster trust, reputation, and legal compliance. We then delved into the key principles of company ethics, such as integrity, transparency, fairness, and accountability, discussing how each contributes to a sound ethical framework.
Examples of ethical companies like Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, and LEGO were highlighted to illustrate how businesses can successfully integrate ethical practices into their operations. We also examined the severe consequences of unethical behavior through cases like Enron and Volkswagen, showcasing the long-term impacts on reputation and financial standing.
The article further provided strategies for maintaining company ethics, including regular ethics training for employees, the importance of ethical leadership, and the role of regular auditing in upholding ethical standards. Additionally, we presented various formats of graphical representation, like charts and infographics, to effectively convey complex data regarding company ethics examples and focus areas.
Call to Action:
This overview underscores the imperative for businesses to adopt and maintain ethical practices. Companies are encouraged to consider not only their financial objectives but also the broader impact of their operations on society and the environment. Embracing ethical practices is not just a legal or moral obligation but a strategic imperative that can drive sustainable growth, enhance brand reputation, and build lasting trust with stakeholders.
Business leaders are urged to lead by example, embedding ethical values into the core of their business strategies. Regular training, transparent communication, and continuous evaluation of ethical practices are essential in fostering a culture of integrity and responsibility.
By prioritizing ethics, companies can contribute positively to the world while achieving their business goals, paving the way for a more just, sustainable, and prosperous future for all.

Conclusion
This exploration into company ethics has underscored its vital role in the modern corporate landscape. We’ve seen how ethics, encompassing principles like integrity, transparency, fairness, and accountability, are not just moral imperatives but foundational elements for long-term business success. The examples of companies like Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, and LEGO highlighted the tangible benefits of embedding ethical practices into business models, including enhanced reputation, customer loyalty, and sustainable growth.
The case studies of Enron and Volkswagen served as cautionary tales, illustrating the damaging and far-reaching consequences of unethical behavior. These examples reinforced the importance of maintaining ethical integrity in all business dealings.
The discussion on strategies for upholding company ethics, such as ethics training, ethical leadership, and regular audits, provided actionable insights for businesses aiming to foster a culture of ethical responsibility.
As businesses continue to navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected global market, the importance of ethics remains paramount. Companies are encouraged to integrate ethical considerations into every aspect of their operations, recognizing that ethical business is not just about avoiding wrongdoing, but about actively doing right by their stakeholders, society, and the environment.
Ultimately, the commitment to company ethics is a commitment to building a more equitable, sustainable, and prosperous future. Businesses, regardless of size or sector, have the opportunity—and responsibility—to lead the way in this endeavor.
References
Here are the references used to provide information on company ethics examples, along with their web addresses:
Ethical Consumer – This source discusses Patagonia’s commitment to workers’ rights, environmental activism, and supply chain management, highlighting how the company operates as a B-Corp.
Web address: www.ethicalconsumer.org
Good On You – This article provides an assessment of Patagonia’s ethical practices, comparing it with other similar brands and rating its performance in various ethical dimensions.
Web address: goodonyou.eco
Yale Insights – This source provides insights into Patagonia’s business model, focusing on their approach to sustainability and collaboration with other companies and industries.
Web address: insights.som.yale.edu
UberArtisan – This article explores Patagonia’s sustainability initiatives, including its use of sustainable materials, carbon footprint reduction efforts, and ethical supply chain management.
Web address: uberartisan.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Company ethics examples
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about company ethics examples, along with their answers:
What are company ethics?
Company ethics, also known as business ethics, refer to the moral principles and standards that guide behavior and decision-making in a business context. These ethics help companies determine what is right and wrong in their operations and interactions with stakeholders.
Why are ethics important in business?
Ethics are crucial in business because they build trust with customers, employees, and the public. Ethical practices enhance a company’s reputation, ensure legal compliance, foster a positive work environment, and contribute to long-term success.
Can you give examples of ethical companies?
Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, and LEGO are often cited as examples of ethical companies. Patagonia is known for its environmental sustainability and ethical labor practices, Ben & Jerry’s for its social justice campaigns and sustainable sourcing, and LEGO for its commitment to product safety and ethical supply chain management.
What are some key principles of company ethics?
Key principles include integrity (honesty and moral uprightness), transparency (openness in operations and communications), fairness (equitable treatment of all parties), and accountability (responsibility for actions and decisions).
How can companies maintain ethical practices?
Strategies for maintaining ethical practices include regular ethics training for employees, ethical leadership from top management, and regular auditing of operations to ensure adherence to ethical standards.
What are the consequences of unethical behavior in business?
Unethical behavior can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, damaged reputation, loss of customer trust, and negative impacts on employee morale. Examples include the Enron scandal and Volkswagen’s emission scandal.
How do ethical practices impact a company’s performance?
Ethical practices can lead to higher employee morale and productivity, increased customer loyalty, and better stakeholder relationships, all of which contribute to improved business performance and sustainability.
Are there any certifications or standards for company ethics?
Yes, certifications like B Corp certification assess a company’s overall social and environmental performance. ISO 26000 guides social responsibility, and the Global Reporting Initiative offers standards for sustainability reporting.
These FAQs cover fundamental aspects of company ethics, offering insights into why ethics matter in business, how they are upheld, and the impact of both ethical and unethical practices.










Leave a Reply